10 Essential Cybersecurity Tools for Every Business
Discover 10 essential cybersecurity tools that will safeguard your business from cyber threats and ensure maximum protection for your data and systems.

If you’re not fully protecting your business from cyber threats, you’re taking a huge risk. Cybersecurity isn’t just a technical concern; it’s essential to the survival of your business. The result of a breach can be severe financial losses, a damaged reputation, and even legal issues.
That’s why it’s so important to take action right away. With the right cybersecurity tools in place, you can protect your business by stopping attacks before they happen and reacting quickly if something does go wrong. Implementing the best methods is your strongest defense, helping to keep your business safe from serious cyber threats.
This guide covers ten essential cybersecurity tools that integrate security into your systems to keep your business and data safe.
10 Essential Cybersecurity Tools for Every Business

1. Endpoint Security
Every device connected to your network whether it’s a phone, desktop, laptop, tablet, or server can be a potential entry point for cybercriminals. As more businesses adopt remote work and allow employees to use their own devices (BYOD), securing these endpoints has become more important than ever. Endpoint security tools are designed to protect these devices from threats, ensuring that one vulnerable device doesn’t compromise your entire network.
How Does It Work?
Endpoint security involves installing software on each device (endpoint) connected to your network. This software monitors, detects, and blocks security threats in real-time. It typically includes antivirus, anti-malware, encryption, and firewall features, all managed from a central platform.
Advanced endpoint security solutions also have Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) capabilities, which continuously monitor device activity, detect advanced threats, and isolate compromised devices to prevent the spread of an attack.
2. Antivirus and Anti-malware
With cyber threats constantly evolving, basic antivirus software just isn’t enough anymore. Modern antivirus and anti-malware tools go beyond scanning for known viruses they actively predict and prevent new threats before they can cause any harm.
How Does It Work?
Modern antivirus software does not just rely on known virus definitions. It uses heuristic analysis to detect new, unknown viruses by analyzing code for suspicious patterns. Additionally, behavior-based detection monitors how files and programs interact with your system, flagging anything that behaves unusually, which could indicate a zero-day attack.
How to Implement Effectively?
First, ensure your antivirus software is configured for real-time protection and automatic updates. However, don't stop there customize the settings to fit your organization’s specific needs. For example, schedule scans during off-peak hours to avoid disruption. Pair your antivirus solution with Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools for a more comprehensive defense, as EDR tools continuously monitor your endpoints and provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
3. Encryption Tools
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect your sensitive data, both at rest and in transit. It ensures that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
How Does It Work?
Encryption converts your data into a secure code, which can only be deciphered by someone with the correct key. This process is important for protecting data stored on devices (data at rest) and data transmitted over networks (data in transit). Advanced encryption tools offer features like full-disk encryption, which protects all the data on a device, and end-to-end encryption, which secures data throughout its entire journey from sender to receiver.
How to Implement Effectively?
Start by identifying which types of data need encryption—typically, this will include customer data, financial information, and intellectual property. Implement full-disk encryption on all devices, especially those used by employees in the field or remote work settings. For data in transit, ensure that all communication channels, such as emails and file transfers, are encrypted using protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security).
Use strong, unique encryption keys and rotate them regularly to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. Additionally, implement a centralized key management system to maintain control over encryption keys and simplify the process.
4. Password Management
Despite advances in cybersecurity, passwords remain a common weak point. Hackers often exploit weak or reused passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems. A powerful password management strategy is essential for maintaining security across your organization.
How Does It Work?
Password managers generate, store, and autofill complex, unique passwords for your accounts. They encrypt these passwords, ensuring that even if the manager is compromised, your credentials remain safe. Many advanced password managers also offer features like password strength analysis and breach monitoring, which can alert you if any of your passwords have been compromised in a data breach.
How to Implement Effectively?
Deploy a password management solution across your organization and enforce its use for all accounts. Educate your team on the importance of creating strong, unique passwords and regularly updating them. Enable password strength analysis and breach monitoring features to ensure that weak or compromised passwords are quickly identified and replaced.
Regularly review and update your password policies, requiring passwords to be a certain length and to include a mix of symbols, numbers, and letters. To further enhance security, integrate your password manager with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) systems, adding another layer of protection.
5. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
As remote work becomes more prevalent, securing your organization’s data as it travels over the internet is important. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure, encrypted tunnel between your network and remote users, safeguarding your data from unauthorized access.
How Does It Work?
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, masking your IP address and ensuring that your online activities remain private and secure. This is especially important when accessing company resources over public Wi-Fi, which is notoriously insecure.
How to Implement Effectively?
Choose a VPN solution that supports powerful encryption protocols, such as OpenVPN or IKEv2/IPSec. Ensure your VPN provider follows a strict no-logs policy, which prevents data from being stored and potentially accessed by unauthorized parties.
Train your team to use the VPN consistently, not just when accessing sensitive data, but whenever they are connected to the internet. Implement split tunneling with caution, as it allows some traffic to bypass the VPN, which can create security gaps. Regularly audit VPN usage logs and monitor for unusual activity that could indicate a compromised connection.
6. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
No matter how strong your defenses are, you should always assume that breaches will happen. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) act as your early warning system, alerting you to potential breaches so you can take swift action.
How Does It Work?
IDS tools monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity. They compare traffic patterns against a database of known threat signatures and use anomaly detection to identify unusual behavior that might indicate a new or unknown threat. There are two main types of IDS: Network-based (NIDS), which monitors traffic across the entire network, and Host-based (HIDS), which monitors activity on individual devices.
How to Implement Effectively?
Deploy IDS at critical points within your network, such as at the perimeter and in front of important servers. Configure the system to generate alerts for any activity that matches known threat signatures or deviates from established norms. Fine-tune the IDS to reduce false positives, which can overwhelm your security team and lead to missed genuine threats. Integrate IDS with your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to correlate alerts with other security data, providing a holistic view of your network’s security.
7. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
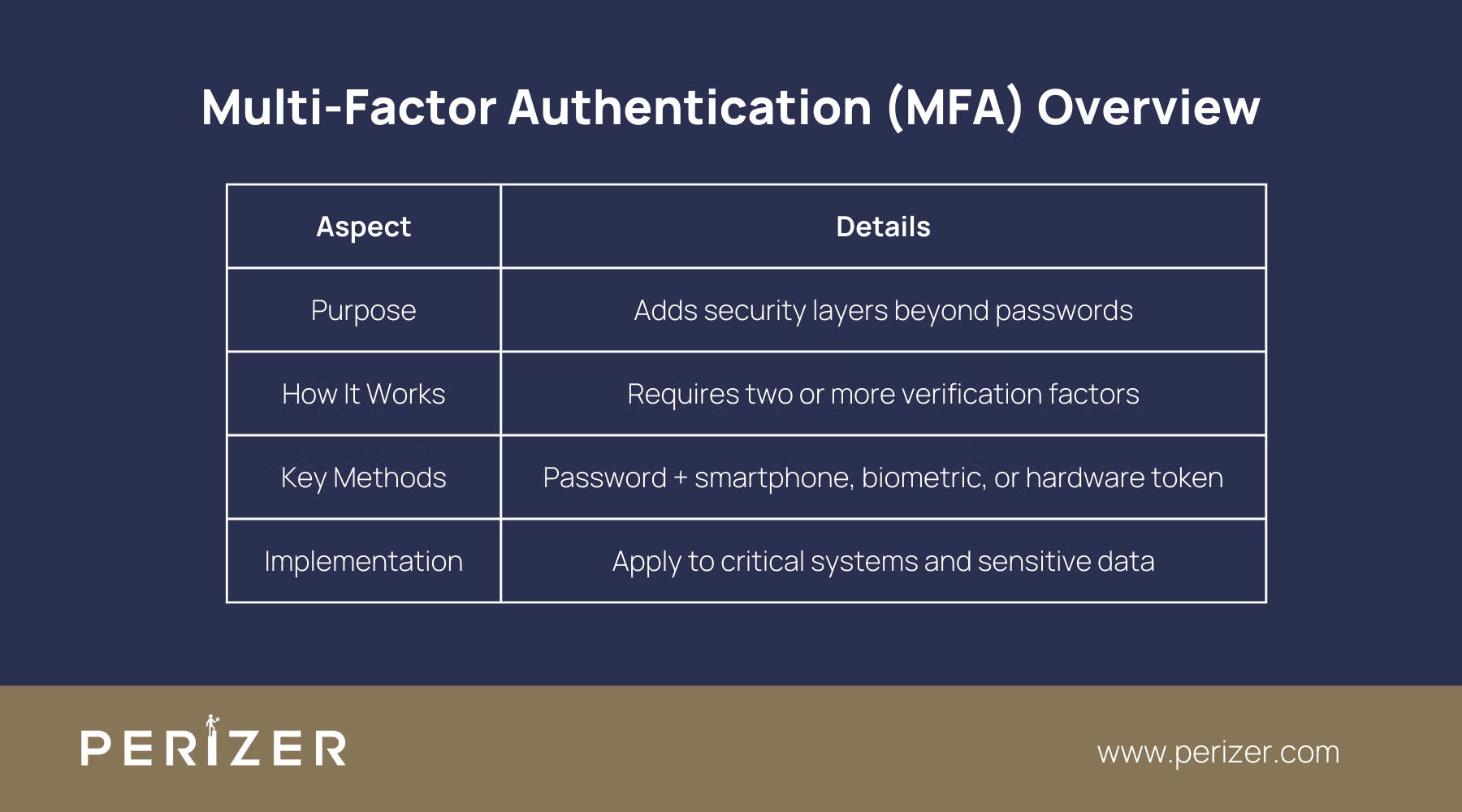
Cybersecurity relying solely on passwords is a risk. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring additional verification steps, making it much harder for attackers to gain access.
How Does It Work?
MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors such as a password, a smartphone, or biometric data before they can access a system. This multi-layered approach ensures that even if a password is compromised, unauthorized access is still unlikely.
How to Implement Effectively?
Integrate MFA into all critical systems and applications, particularly those containing sensitive data. Choose an MFA solution that supports various authentication methods, allowing you to tailor the approach based on user needs. For example, implement biometric verification for high-risk users and hardware tokens for others.
Regularly review your MFA methods and consider adopting emerging technologies like behavioral biometrics, which analyze patterns in how users interact with their devices. Ensure that MFA is mandatory for all remote access and high-privilege accounts, providing a powerful line of defense against unauthorized entry.
8. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Managing security across a complex network can be overwhelming. SIEM solutions streamline this process by centralizing security monitoring, collecting, and analyzing log data from various sources in real time.
How Does It Work?
SIEM tools aggregate log data from servers, firewalls, IDS/IPS, and other security devices, analyzing it for patterns that could indicate a threat. They use correlation rules to detect suspicious behavior, triggering alerts when potential threats are identified. Advanced SIEM solutions also incorporate threat intelligence feeds, which provide context to alerts by comparing them against known threat indicators.
How to Implement Effectively?
Identify the significant systems and devices that will feed data into your SIEM. Configure the SIEM to collect logs from all relevant sources, ensuring comprehensive coverage of your network. Develop and fine-tune correlation rules to align with your organization’s specific threat landscape. For example, create a rule that triggers an alert if an unusual login attempt is followed by an attempt to access sensitive data. Regularly review and update these rules to stay ahead of emerging threats. Use the SIEM’s reporting capabilities.
9. Patch Management Tools
Outdated software is one of the most common vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. Patch management tools ensure that your systems and applications are always up-to-date with the latest security patches, minimizing the risk of attacks.
How Does It Work?
Patch management tools like SolarWinds Patch Manager or Microsoft WSUS automate the process of identifying, downloading, and installing patches for your software and operating systems. These tools regularly scan your systems for missing patches and deploy them as soon as they are available, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
How to Implement Effectively?
Start by conducting a thorough inventory of all software and systems within your network. Implement a patch management tool that automates patching across different platforms and applications. Schedule regular scans to detect and apply missing patches promptly. For critical systems, test patches in a controlled environment before deploying them network-wide to ensure they do not disrupt operations. Regularly review patch reports to confirm that all systems are up-to-date and that no patches have been missed.
10. Email Security
Email remains one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks, including phishing, spam, and malware. To protect your business, it's essential to implement strong email security measures that go beyond basic filters.
How Does It Work?
Email security tools use advanced algorithms and machine learning to detect and block malicious emails before they reach your inbox. These tools filter out spam, phishing attempts, and emails containing viruses or malware. They also provide features like encryption for sensitive communications and can identify unusual email behavior, flagging potential threats in real-time.
How to Implement Effectively?
Choose an email security solution like Proofpoint or Mimecast that offers powerful automated filters to catch spam, phishing, scams, and viruses. Make sure it includes encryption options, such as Virtru or Zix, for sensitive emails to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly update the filters to adapt to new and emerging threats.
However, no filter is foolproof, so it’s important to complement these tools with employee training. Educate your team on how to recognize suspicious emails, such as unexpected attachments or requests for sensitive information, and establish a clear process for reporting these emails to IT. Regular phishing simulations using tools like KnowBe4 can help reinforce this training and keep your team vigilant against email-based threats.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is more than just a technical necessity; it’s an important aspect of running a secure and successful business. Implementing these cybersecurity tools is important for safeguarding your data and building a resilient defense strategy that ensures long-term business success.
It’s important to remember that setting up these tools is just the beginning. Regular updates, continuous monitoring, and ongoing training for your team are essential to staying ahead of potential threats. By taking a proactive approach, you can prevent small vulnerabilities from becoming major security breaches, keeping your business safe and resilient.
FOCUSED, FAST, GOVERNMENT READY
Stay Tuned With Our Latest Insights

Staff Augmentation
Learn how to select the perfect IT outsourcing partner to promote your team’s capabilities, improve productivity, and drRead more...

Staff Augmentation
Find the perfect staff augmentation partner by aligning your goals, evaluating expertise, managing costs, and ensuring aRead more...

Cyber Security
We focus on understanding the needs, behaviors, and expectations of your users through extensive user research. This infRead more...