8 Steps to Protect Data Privacy in Your Business
Strengthen your business with 8 advanced steps to safeguard data privacy, protect against breaches, and maintain customer trust.

Data privacy has become an important concern as businesses handle an ever-growing amount of sensitive information. The increased volume of data doubled with the complexity of cyber threats, makes organizations more unprotected from breaches. Cybercriminals are constantly refining their tactics to exploit weaknesses, putting customer trust and business operations at risk.
To truly safeguard your business’s sensitive data, you need to go beyond compliance and integrate strong security practices into your daily operations. Ignoring this can result in costly breaches, lost customer trust, and serious damage to your reputation issues that can be hard to recover from. Without strong data privacy measures, your business risks not only legal trouble but also losing the confidence of your customers. Protecting your data is essential to maintaining the trust and credibility that your business depends on.
In this guide, we’ll highlight eight key steps to strengthen your data privacy practices, helping you protect sensitive information, build customer trust, and safeguard your business from costly breaches.
Monitoring and ResponMonitoring and Responding to Data Breachesding to Data Breaches
Monitoring and Responding to Data Breaches
8 Steps to Protect Data Privacy in Your Business

1. Embedding Privacy Regulations into Your Operations
Knowing the details of regulations like GDPR and CCPA is important, but the key is integrating these laws into your business operations seamlessly. Compliance should be more than just meeting legal requirements it should become part of your business culture.
How to Implement Privacy Regulations?
Start by thoroughly auditing your data collection practices. Examine each piece of data you collect and determine if it’s necessary. GDPR's principle of data minimization is about more than just reducing data collection. it’s about strategically minimizing your risk. Automate this process where possible, so your system continuously flags and reduces unnecessary data collection.
Next, update your privacy policies to reflect your refined practices. Don’t let these policies become outdated make sure they evolve as your business does. Use clear, simple language that your customers can understand, building trust through transparency.
Regularly review and revise these policies to stay aligned with any regulatory changes or shifts in your business practices. Training your employees on these updated policies is also crucial, as each department needs to understand how privacy affects their specific roles. Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance and risk management can help ensure these practices are consistently applied.
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Data Audit
To protect your data effectively, you need a clear understanding of what data you have, where it’s stored, and how it’s used. A comprehensive data audit is essential for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring all data is adequately protected.
How to Perform an Effective Data Audit?
Start by mapping out all the data sources in your organization, including customer data, employee records, and financial information. Document how data flows through your organization, from collection to storage, and determine who has access to it. This step isn’t just about creating an inventory it’s about understanding how data moves through your business and identifying any weak points in your data management practices. Use automated tools to help scan and map these data flows, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
Focus on uncovering any hidden data that might have been missed during regular data management. These overlooked data points can act as significant risks if left unsecured. Once identified, secure or properly dispose of this data to eliminate potential vulnerabilities. Regularly conduct these audits, adapting to any changes in your business operations or technology landscape.
Finally, evaluate where your data is stored whether on local servers, in the cloud, or external devices. Don’t assume these storage methods are secure actively verify that they meet current security standards. If they don’t, take immediate steps to bring them up to par.
3. Classify and Organize the Data
Not all data is equally sensitive. By classifying and customizing your data based on its level of sensitivity, you can focus your security efforts where they matter most, ensuring that your most critical assets are protected from threats.
How to Classify and Customize Your Data?
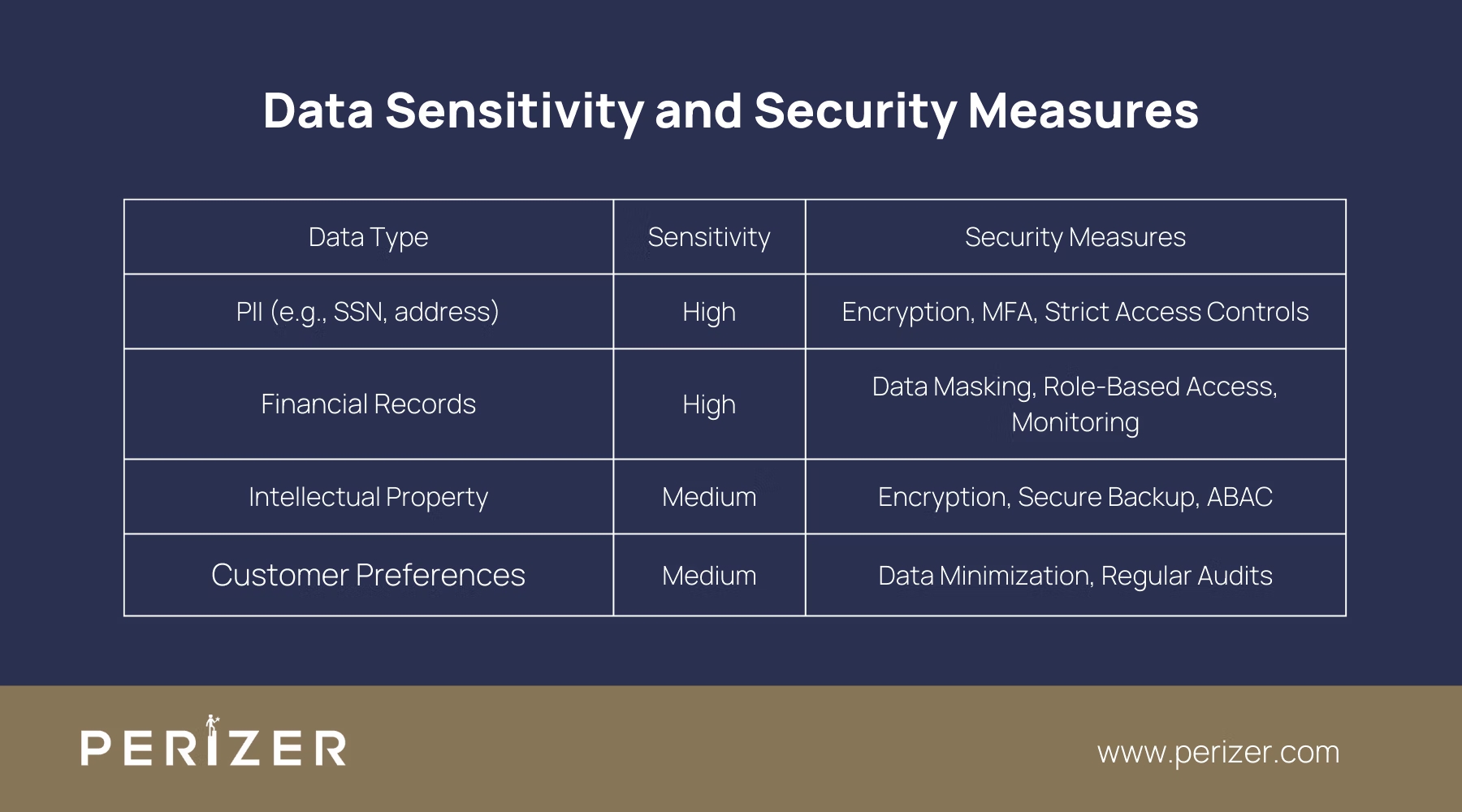
Develop a data classification framework customized to your business needs using tools like Spirion or Boldon James. Sort data into categories of low, medium, and high sensitivity. For instance, personally identifiable information (PII) and financial records should be classified as high sensitivity due to the severe consequences of a potential breach.
Once classified, apply security measures that match the data’s sensitivity level. High-sensitivity data requires the strictest controls, such as advanced encryption, rigorous access restrictions, and continuous monitoring. Regularly review and update your classification framework to ensure it adapts to new types of data or changes in regulations.
To streamline this process, use automated tools that tag data with the appropriate classification as it’s created or modified. This ensures that your data is consistently handled according to your security protocols.
4. Strengthen Access Controls
Controlling who can access your data is one of the most effective ways to protect it. Unauthorized access is a major cause of data breaches, so implementing strong access controls is essential.
How to Implement Strong Access Controls?
Start by implementing role-based access control (RBAC) using tools like Okta or Centrify. Assign access rights based on each employee’s role, ensuring they can only access the data necessary for their job. For example, an HR manager might need access to employee records but should not have access to customer financial data. Regularly review and update these access rights, especially when employees change roles. Conduct periodic audits to ensure that the current access levels are still appropriate.
For highly sensitive data, consider using attribute-based access control (ABAC). ABAC adds a layer of protection by considering factors like time of access, location, and the device being used. This ensures that sensitive data is accessed only under secure conditions. ABAC’s flexibility allows it to adapt access controls dynamically based on real-time risk assessments.
To further enhance security, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to confirm their identity through multiple methods such as a password and a code sent to their phone. This additional security layer significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. MFA should be mandatory for anyone accessing high-sensitivity data or critical business systems.
5. Encrypt Data to Prevent Unauthorized Access
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to secure your data, ensuring that even if it’s intercepted, it remains unreadable. To maintain the privacy and integrity of your data, powerful encryption practices are essential.
How to Effectively Encrypt Your Data?
Ensure that all sensitive data is encrypted both at rest (when stored) and in transit (when being transmitted). Use strong encryption standards like AES-256 for data at rest and secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL for data in transit. Encryption should be a default measure for any data classified as medium or high sensitivity.
Proper management of your encryption keys is just as important as the encryption itself. Store your encryption keys separately from the data they protect, ideally in a hardware security module (HSM). Regularly rotate these keys and restrict access to them, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access. Conduct regular audits to verify that your encryption practices are up-to-date with the latest security standards.
Extend encryption to your backup data as well. This ensures that even if your backup storage is compromised, the data remains secure. Regularly test your encryption processes to confirm that data can be decrypted effectively by authorized users.
6. Secure Data Retention to Prevent Recover
When data is no longer needed, simply deleting it isn’t enough. You must ensure that it’s disposed of securely, leaving no possibility for recovery, which could lead to unauthorized access.
How to Ensure Secure Data Disposal?
Create a data retention policy that specifies how long different types of data should be kept and when they should be securely deleted. Align this policy with legal requirements and your business needs. Automate the data deletion process where possible to minimize the risk of human error and ensure consistency across your organization.
For digital data, use software that overwrites it multiple times, making it irrecoverable. For physical media like hard drives or paper documents, use secure methods such as shredding or degaussing (erasing magnetic fields) to ensure that data cannot be reconstructed. Always verify that data has been securely destroyed. If you rely on third-party disposal services, obtain certificates of destruction and periodically audit their processes to ensure they meet your standards.
7. Implement Data Privacy Techniques
Data privacy protects sensitive information by hiding real data within your systems, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. This technique is especially valuable in environments like testing and development, where data needs to be used without exposing actual sensitive information.
How to Implement Data Masking?
Identify the data that requires masking this typically includes PII, financial information, and other sensitive categories. Use data masking tools like Delphix or Informatica to replace real data with realistic but fictitious data within your databases. For production environments, implement dynamic data masking, which automatically masks data for unauthorized users, ensuring that only those with the proper credentials can view the real data.
8. Monitor and Respond to Data Breaches
Even with the best safeguards in place, data breaches can happen. Your ability to respond quickly and effectively can make all the difference in minimizing damage.
How to Monitor and Respond to Data Breaches?
Implement continuous monitoring systems that track data activity and alert you to any suspicious behavior. Use advanced tools like Splunk or LogRhythm for Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) to aggregate data from multiple sources and provide real-time analysis
Develop a detailed breach response plan. Outline the steps your team must take immediately following a breach, including isolating affected systems, conducting a thorough investigation, and notifying all affected parties customers, employees, and regulatory authorities. Make sure everyone on your team knows their role in this plan, and regularly test it through simulations to ensure preparation.
After a breach, conduct a thorough review to understand what went wrong and how you can improve your defenses. Use these insights to update your data protection strategies, making your business more resilient to future attacks.
By following these advanced steps, you can significantly strengthen your data privacy practices, protect your business from potential breaches, and ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
Conclusion
.Advanced data privacy strategies are essential for any business seeking to protect sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and ensure long-term success in an increasingly digital and threat-load environment. To protect your business, embed privacy practices into every aspect of your operations. Conduct thorough data audits, classify sensitive information, and strengthen access controls with strong encryption.
Additionally, securely dispose of unnecessary data, use data masking, and maintain continuous monitoring to stay ahead of potential breaches. By following these eight steps, you’ll not only meet regulations but also protect your reputation and earn your customers’ trust.
FOCUSED, FAST, GOVERNMENT READY
Stay Tuned With Our Latest Insights

Staff Augmentation
Learn how to select the perfect IT outsourcing partner to promote your team’s capabilities, improve productivity, and drRead more...

Staff Augmentation
Find the perfect staff augmentation partner by aligning your goals, evaluating expertise, managing costs, and ensuring aRead more...

Cyber Security
We focus on understanding the needs, behaviors, and expectations of your users through extensive user research. This infRead more...